Introduction
Test methods for residual solvents in pharmaceuticals are specified in the USP (United States Pharmacopeia) General Chapter <467> Residual Solvents, which mainly specifies using the headspace GC method. Residual solvents in pharmaceuticals are classified into Classes 1 to 3 based on potential risks to human health and strictly controlled accordingly. Sensitive analysis is required. The carrier gas generally used for analysis is He, but the depletion of He has become a problem recently. Consequently, there is a need for using an alternative carrier gas such as H2 for analysis. Any method changes, such as substituting He with an alternate carrier gas, must be validated according to USP Chapter <1467> Residual Solvents—Verification of Compendial Procedures and Validation of Alternative Procedures.
This paper presents the results of using H2 as a carrier gas with an HS-20 NX headspace sampler to analyze Class 1 and 2 watersoluble samples in accordance with USP General Chapter <467> Residual Solvents.
*Analytical samples were prepared using a different procedure fromthe USP to confirmthe performance of the apparatus.
Instrument Configuration and Analysis Conditions
A Nexis GC -2030 gas chromatograph and Shimadzu HS-20 NX headspace gas sampler were connected to measure the listed Class 1 and Class 2 standard solutions according to USP General Chapter <467> Residual Solvents, Procedure A. The analytical conditions for GC and HS are indicated in Table 1.
Table 1 Water-Soluble Sample Analysis Conditions
GC Analysis Conditions (Procedure A)
Model: Nexis GC-2030
Detector: FID-2030 flame ionization detector
Column: SH-Rxi™-624 Sil MS (0.32 mm I.D.×30 m, d.f.= 1.8 μm)
Column Temperature: 40 °C (20 min) – 10 °C/min – 240 °C (20 min) Total 60 min
Injection Mode: Spilt 1:5
Carrier Gas Controller: Constant linear velocity mode (H2 and He)
Linear Velocity: 35 cm/sec
Detector Temperature: 250 °C
FID H2 Flowrate: 32 mL/min
FID Make-up Flowrate: 24 mL/min (N2)
FID Air Flowrate: 200 mL/min
HS Analysis Conditions (Procedure A)
Oven Temperature: 80 °C
Sample Line Temperature: 110 °C
Transfer Line Temperature: 120 °C
Vial Stirring: Off
Vial Volume: 20 mL
Vial Heat-Retention Time: 45 min
Vial Pressurization Time: 1 min
Vial Pressure: 75.0 kPa(N2)
Loading Time: 0.5 min
Needle Flush Time: 5 min
Injection Volume: 1 mL
Load Equilib. Time: 0 min
Analysis of Class 1 Standard Solution (Water-Soluble Sample)
The analysis results for Procedure A using a H2 carrier are shown in Fig. 1. The S/N ratio and repeatability values for each peak are shown in Table 2. Table 3 shows the S/N ratio and repeatability values for each peak when using a He carrier as a reference.
Using a H2 carrier, the results obtained with Procedure A satisfied the requirements of the USP, which specifies that "the S/N ratio for 1,1,1-trichloroethane in the Class 1 standard solution is not less than 5."
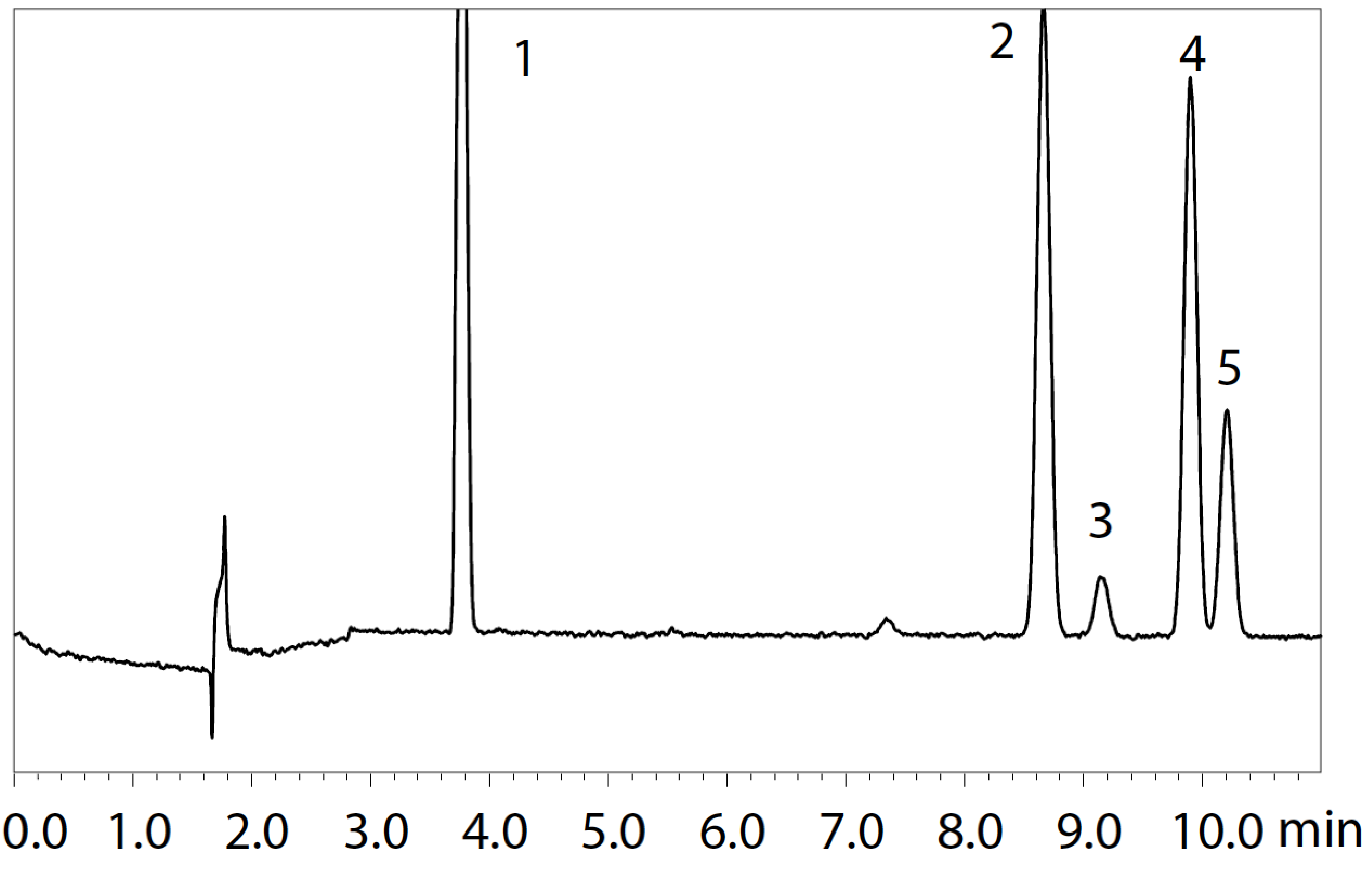
| Peak | Compound | S/N Ratio*1(n=4) | %RSD*1(n=4) |
| 1 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 93 | 1.99 |
| 2 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | 123 | 1.45 |
| 3 | Carbon tetrachloride | 15 | 3.94 |
| 4 | Benzene | 145 | 2.48 |
| 5 | 1,2-Dichloroethane | 57 | 2.60 |
Table 2 S/N Ratio and Repeatability of Class 1 Standard Solution (Procedure A) Using H2 Carrier
| Peak | Compound | S/N Ratio*1(n=4) | %RSD*1(n=4) |
| 1 | 1,1-Dichloroethane | 131 | 1.44 |
| 2 | 1,1,1-Trichloroethane | 150 | 1.64 |
| 3 | Carbon tetrachloride | 13 | 7.30 |
| 4 | Benzene | 188 | 0.66 |
| 5 | 1,2-Dichloroethane | 76 | 0.81 |
Table 3 S/N Ratio and Repeatability of Class 1 Standard Solution (Procedure A) Using He Carrier
*1 The S/N ratio and relative standard deviation (%RSD) values are reference values and not intended to be guaranteed values.
Analysis of Class 2 Standard Solution (Water-Soluble Sample)
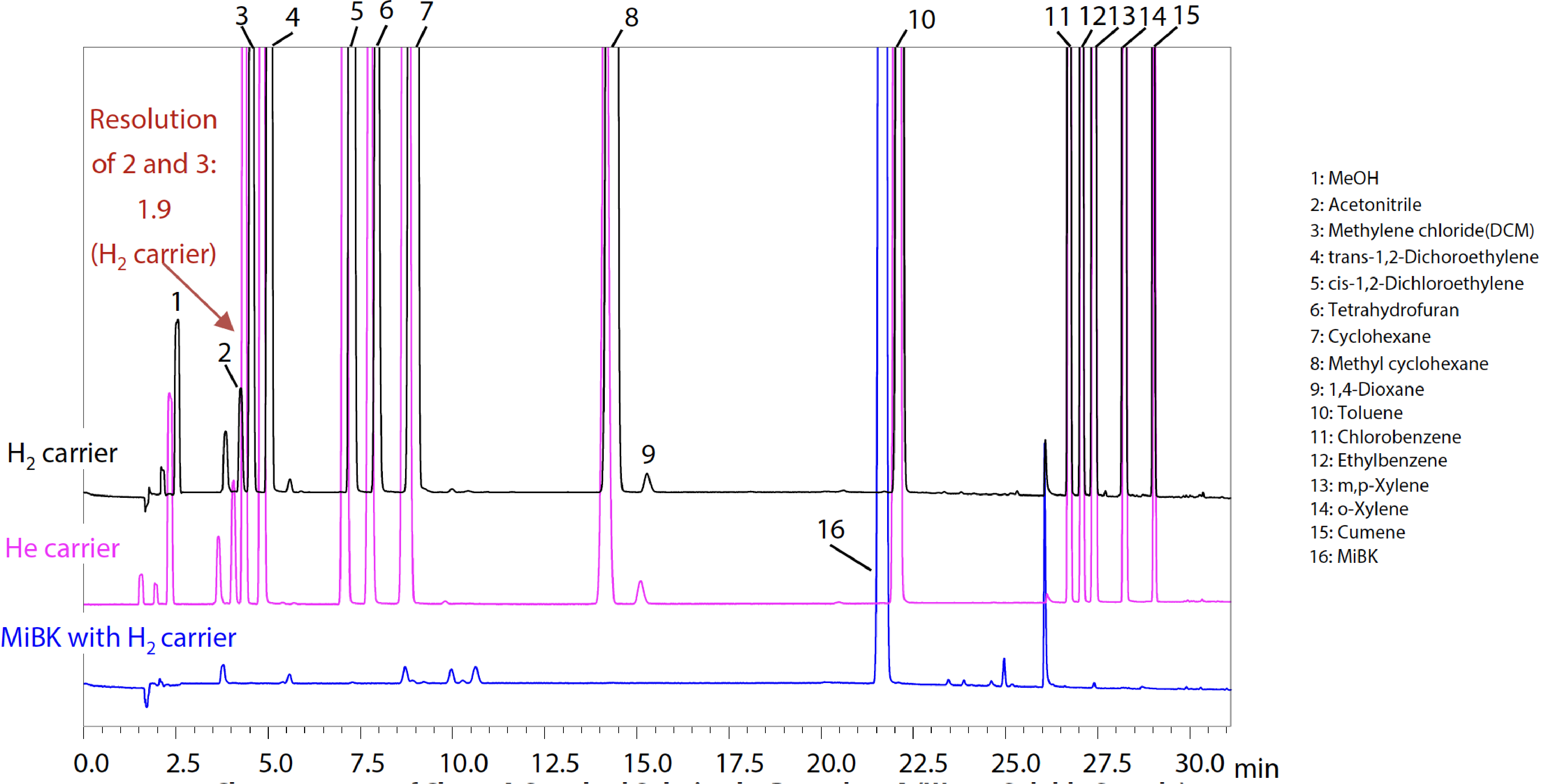
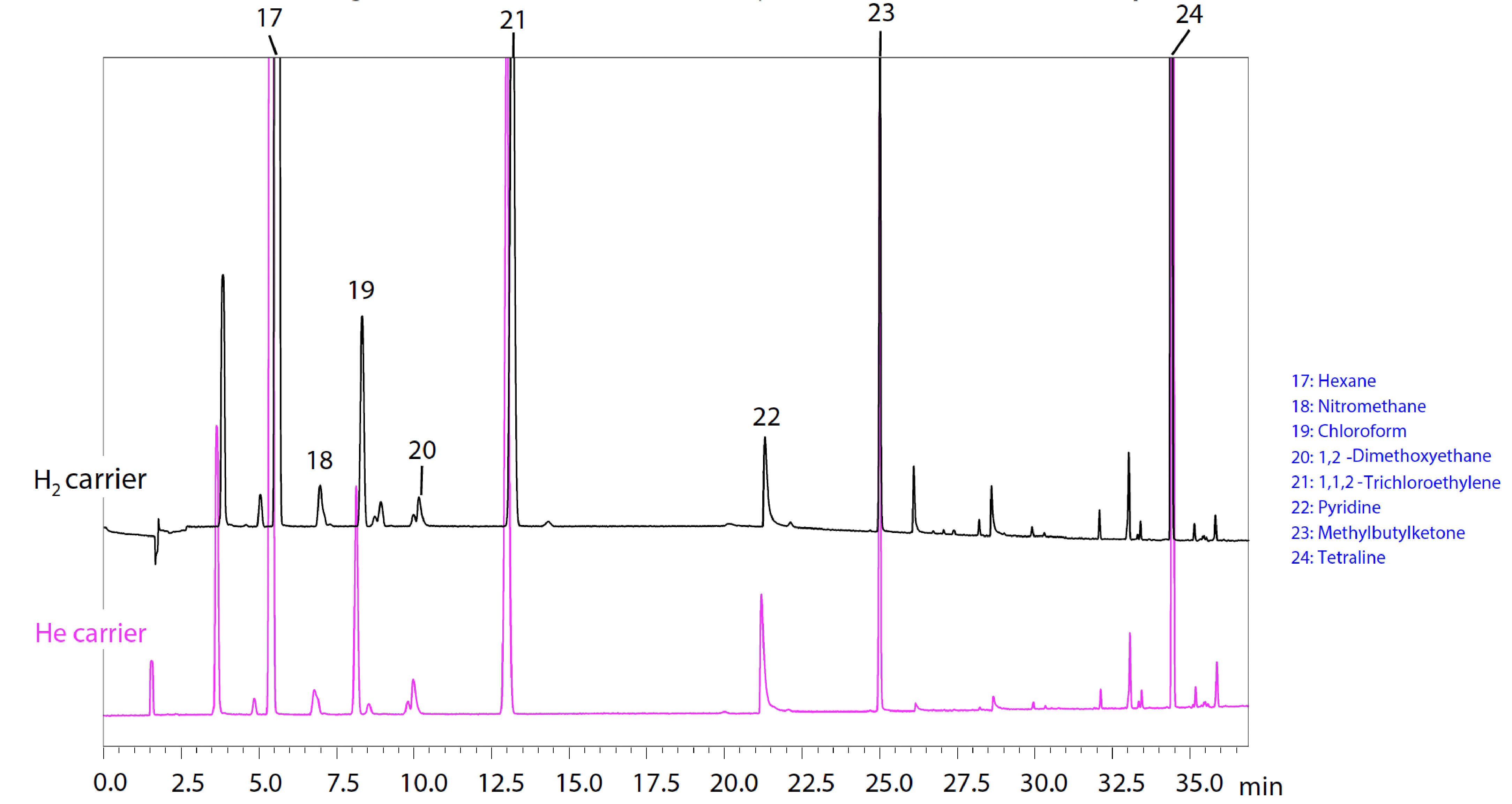
Fig. 2 shows the analysis results for a Class 2A and Fig. 3 for a Class 2B standard solution. Methyl isobutyl ketone (MiBK), a component newly added to USP General Chapter <467> Residual Solvents for Class 2A was also measured. (Results with the H2 carrier are indicated in black, the He carrier in pink, and for MiBK with the H2 carrier in blue.) Satisfactory system suitability results were also obtained, for which the USP specifies that “the resolution between acetonitrile and methylene chloride in the Class 2A standard solution is not less than 1.0“ when using Procedure A.
*The resolution values shown in Fig. 2 are intended as reference values and are not guaranteed.
Conclusion
Using a H2 carrier gas, the analysis achieved the accuracy levels required by USP Chapters <467> and <1467>. The Nexis GC- 2030 features a hydrogen sensor to ensure safe H2 usage. Hydrogen sensors detect potential leaks early. When hydrogen leakage increases, the main power supply is switched off to prevent accidents. Using a H2 carrier can help reduce lab costs. For information about using a N2 carrier for analysis of residual solvents in pharmaceuticals using water-soluble samples, refer to Application News No. G325.




